Neurological Disorders
Neurological Disorders and Chinese Medicine
Examples of neurological conditions that Chinese medicine resolves effectively includes pain syndromes, paralysis, stroke, and brain disorders. According to Chinese medical theory, these conditions can be caused by trauma, emotions, pathogens, malnourishment, Yin or Yang Deficiency, and/or improper lifestyle habits. For best outcomes using self-care, combine associated Aroma Acu-Sticks® to acu-points, topical remedies, and good lifestyle practices.
Related Articles:
![]()
Acupressure for Neurological Pain
- Apply the Earth Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Spleen 10
- Apply the Metal Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Large Intestine 4
- Apply the Wood Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point Liver 3
- Apply the Fire Element Acupressure Stick to Acupressure Point San Jiao 5
![]()
Symptoms of Neurological Disorder by Muscle Innervation
This is a clever way to "reverse engineer" Chinese medical diagnosis and help to narrow down the causes of pain and disease according to Chinese medicine.
Acupuncture channels run through specific muscles that connect to specific nerves; Chinese medical theory identifies "muscle regions" associated with "Channel Theory". This allows for a different perspective when choosing acupressure points by associating symptoms to acupressure channels.
Like all diagnostic tools used in Chinese medicine, this is just one clue to identifying underlying causes of pain and disease; you would put these signs together with other indications of imbalances to form a full understanding of the "root", or causative, factors of bodily disorders. While not an exhaustive list, these are helpful factors in finding the appropriate acupressure points for your health condition.
Lung (LU) Channel Symptoms: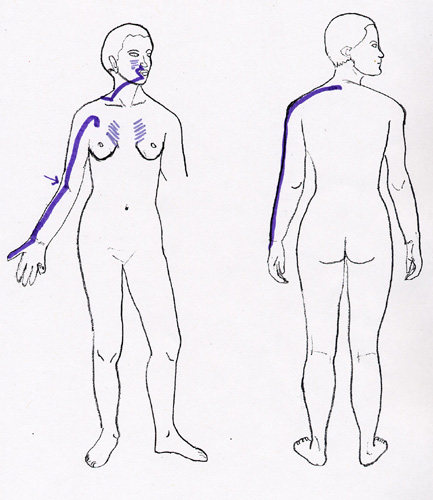
- Arthritis of thumb
- Pain of the arm
- Tendonitis of abductor/flexor pollicis bravis
- Lateral epicondylitis
- Bicepital tenosynovitis or tendonitis
- Stiff neck
- Whiplash injury
- Chest pain
Large Intestine (LI) Channel Symptoms:
- Mouse Finger-Tenosynovitis or arthritis of index finger-Trigger pointer finger
- Pain of arm or shoulder
- Pain of teeth
- Sinus pain
- Tendonitis of abductor pollicis bravis
- Bicepital tenosynovitis or tendonitis
- Tear or tendonitis of supraspinatus
- Lateral epicondylitis
- Acromion-Clavicle separation
- Cervical disc pain
- Bell’s palsy
- Ear pain-Otitis Media
- Skin diseases such as hives, psoriasis, eczema
Stomach (ST) Channel Symptoms
- Stomach pain
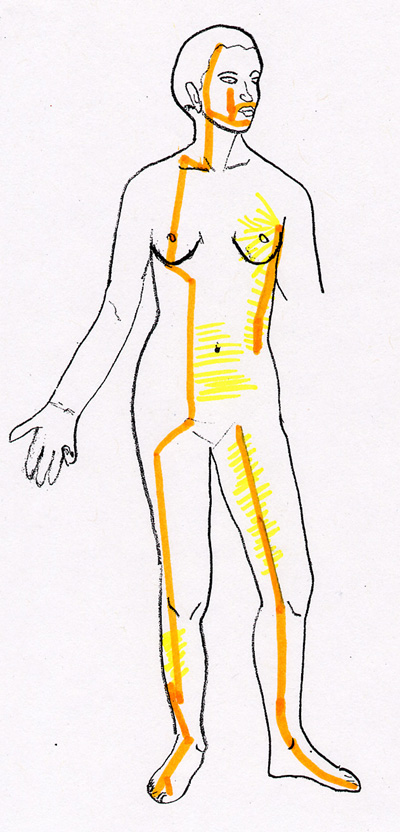
- Sinus pain
- Face pain
- Iliopsoas
- Hip flexor
- Quadriceps
- Medial and lateral menisci
- Patella
- Patellar tendon
- Femoral condyles
- Shin splints
- Morton’s neuroma
- Inguinal hernia
Spleen (SP) Channel Symptoms:
- Low back pain
- Breast pain
- Pain of big toe
- Iliopsoas
- Medial meniscus
- Medial collateral
- Patella
- Patellar tendon
- Shin splints
- Medial ankle sprains
- Gout
![]()
Kidney (KI) Channel Symptoms:
- Baker’s cyst

- Medial calf injuries-high level-origin
- Compartment syndrome-RSD
- Hamstring injuries-low level-insertion
- Achilles strains
- Plantar fasciitis
- Morton’s Neuroma
Bladder (BL) Channel Symptoms:
- Low back pain
- Head pain
- Anterior cruciate ligament-ACL
- Posterior cruciate ligament-PCL
- Baker’s cyst
- Lateral calf injuries-high level-origin -Compartment syndrome
- Hamstring injuries-low level-insertion
- Achilles strains
- Plantar fasciitis
![]()
Gallbladder (GB) Channel Symptoms:
- SI joint pain
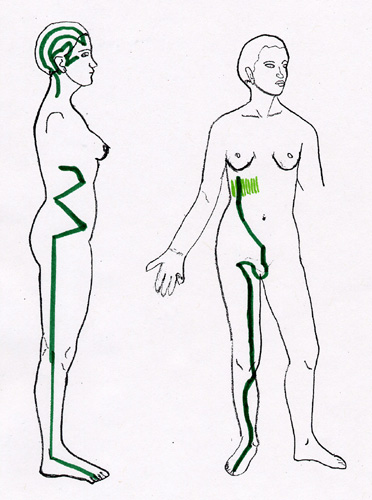
- Sciatica
- Lateral collateral ligament-LCL
- Lateral meniscus
- Illio-tibial band injury
- Tibio-fibular ligament injury
- Lateral muscle injuries-Vastus lateralis
- Lateral ankle sprains
Liver (LV) Channel Symptoms:
- IT band pain and tightness
- Inguinal hernia
- Medial collateral ligament-MCL
- Medial muscle injuries-Vastus Medialis
- Goose foot, pes anserinus (PA), Gracilis, Satorius, Semi-tendinosus,
- Semimebranous innervates with the tibial nerve and is located at the superior lateral quadrant of the ischial tuberosity is responsible for the extension of the thigh, flexes the knee, and also rotates the tibia medially, especially when the knee is flexed.
- Gout
- Medial ankle sprains
![]()
Sanjiao (SJ) Channel Symptoms:
- Tendonitis of extensor digitorium-middle finger pain
- Tricepital tendonitis
- Tear or tendonitis of teres minor and infraspinatus
- Lateral epicondylitis
- Elbow dislocation
- Olecranon bursitis
- Trapezius stress (RSI)
- Migraines and tinnitus
- Ear pain
Small Intestine (SI) Channel Symptoms: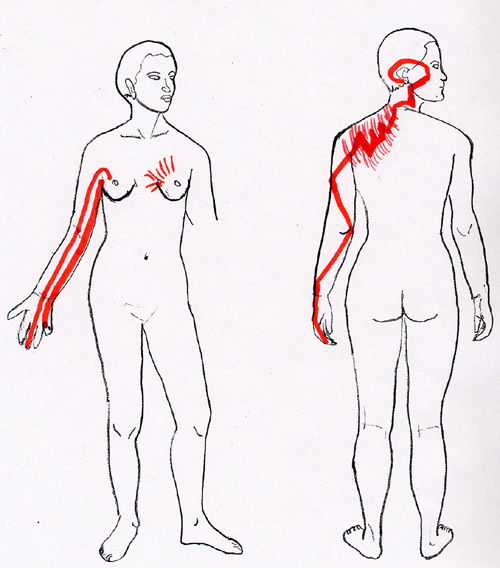
- Neck pain
- Spine and back pain
- Tennis elbow
- Tendonitis of flexor palmaris
- Medial epicondylitis
- Ulnar nerve disfunction
- Tendonitis of infraspinatus, teres minor and subscrapularis
- TMJ
- Brain concussion
- Vertigo
Pericardium (PER) Channel Symptoms:
- Arthritis of middle and ring fingers-Trigger fingers
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Bicepital tenosynovitis or tendonitis
- Dupuytren’s disease/Tendon contracture
- Chest pain-cardiac or non-cardiac
- Arrhythmia or anxiety attacks
- Nausea or vomiting
- GERD
Heart (HT) Channel Symptoms:
- Heart pain
- Pinky finger pain
- Pain of the palm of the hand-tendonitis of flexor palmaris
- Medial epicondylitis
- Ulnar nerve dysfunction
- CNS disorders such as seizures, cerebral palsy
- Palpitations
- Insomnia
- Emotional distress
- ADD or ADHD
![]()
Guo X, Ma T. Effects of Acupuncture on Neurological Disease in Clinical- and Animal-Based Research. Front Integr Neurosci. 2019 Aug 30;13:47. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2019.00047. PMID: 31543763; PMCID: PMC6729102.
Park H. K., Lee H. (2010). Advanced acupuncture system for neurological disorders. Neurol. Res. 32, 3–4. 10.1179/016164109x12537002793607
Zhou J., Peng W., Xu M., Li W., Liu Z. (2015). The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for patients with Alzheimer disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine94:e933. 10.1097/md.0000000000000933
Li X., Chen C., Yang X., Wang J., Zhao M. L., Sun H., et al. . (2017). Acupuncture improved neurological recovery after traumatic brain injury by activating BDNF/TrkB pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017:8460145. 10.1155/2017/8460145
Wang Y, Li W, Peng W, Zhou J, Liu Z. Acupuncture for postherpetic neuralgia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Aug;97(34):e11986. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011986. PMID: 30142834; PMCID: PMC6113033.
This information has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This information is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
